

AMAZING WORLD


All Rights Reserved © 2012 by boomingsites.com | Designed & Developed by Tep Samnang

SPONSORS
Post Your Banners & Logo
Please Contact: (855)77-700-711
postads@boomingsites.com
Please Contact: (855)77-700-711
postads@boomingsites.com
SUPER



Reflection
Beauty Salon
Best
For
Your
Choice!
Beauty Salon
Best
For
Your
Choice!

$10 per month
242 x 143
(Free, one Product/Service Post, one Page, Full Design & Link Page/Site)


www.boomingsites.com
www.boomingsites.com
www.boomingsites.com
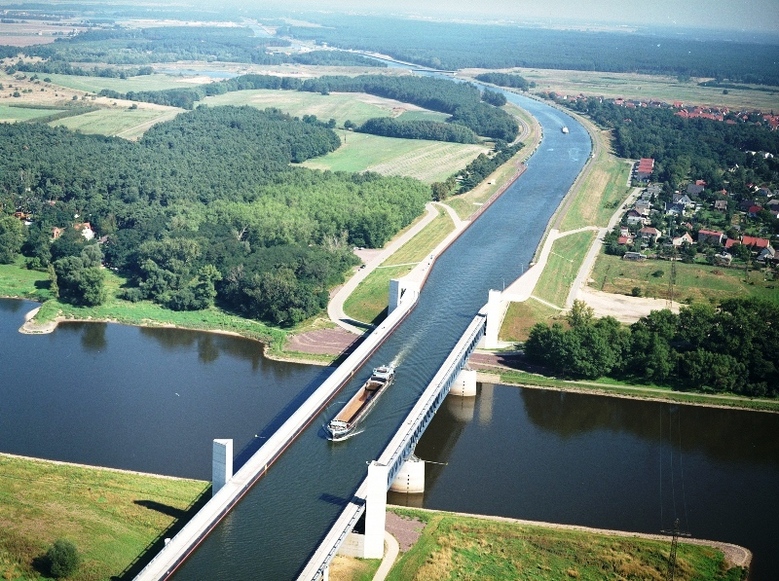
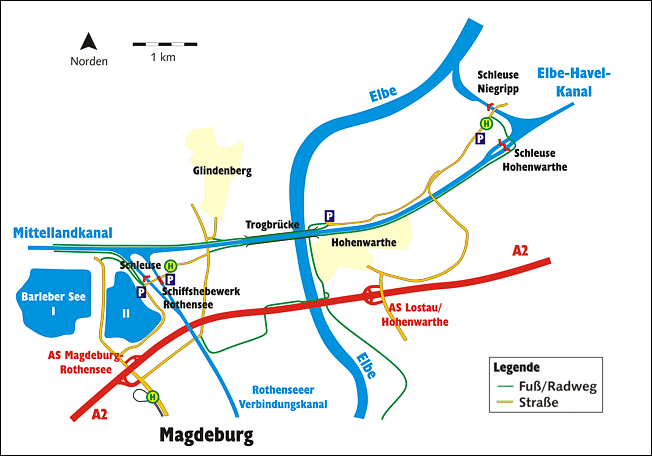
Magdeburg Water Bridge (Germany): Largest Water Bridge in Europe
Just over the Elbe River, this one-of-a-kind structure joins two significant German shipping canals, the Elbe-Havel Canal and the Mittelland Canal. It is also the longest passable aqueduct in the world, spanning 918 meters. It was built as part of the German reunification project.
Throughout amost 1 km, this 500 million euros worth water bridge, allows carrier to avoid the crowded long canal along the Elbe. The shipping often have a problem on this bridge when the water is at the lowest level.
Just over the Elbe River, this one-of-a-kind structure joins two significant German shipping canals, the Elbe-Havel Canal and the Mittelland Canal. It is also the longest passable aqueduct in the world, spanning 918 meters. It was built as part of the German reunification project.
Throughout amost 1 km, this 500 million euros worth water bridge, allows carrier to avoid the crowded long canal along the Elbe. The shipping often have a problem on this bridge when the water is at the lowest level.
The Elbe–Havel Canal and Mittelland Canal canals had previously met near Magdeburg but on opposite sides of the Elbe, which was at a significantly lower elevation than the two canals. Ships moving between the two had to make a 12-kilometre (7.5 mi) detour, descending from the Mittelland Canal through the Rothensee boat lift into the Elbe, then sailing downstream on the river, before ascending to the Elbe-Havel Canal through Niegripp lock. Low water levels in the Elbe often prevented fully laden canal barges from making this crossing, requiring time-consuming off-loading of cargo.
The reunification of Germany and establishment of major water transport routes made the Water Bridge a priority again. Work started in 1997, with construction taking six years and costing €500 million. The water bridge now connects Berlin’s inland harbour network with the ports along the Rhine river. The aqueduct's tough structure incorporates 24,000 tonnes of steel and 68,000 cubic meters of concrete.
In addition to the bridge, a double lock was constructed to allow vessels to descend from the level of the bridge and Mittelland Canal to that of the Elbe-Havel Canal.
